Ar2CorD Project Update: Two Articles Published
As part of Ar2CorD project two articles have been published in high impact scientific journals as part of the deliverables.
As part of Ar2CorD (Low carbon concrete for Arctic climate with excellent durability and sustainability) project, the work package 1 of the project is being coordinated by Priyadharshini Perumal and Adeolu Adediran. So far, two articles have been published in high impact scientific journals as part of the deliverables.
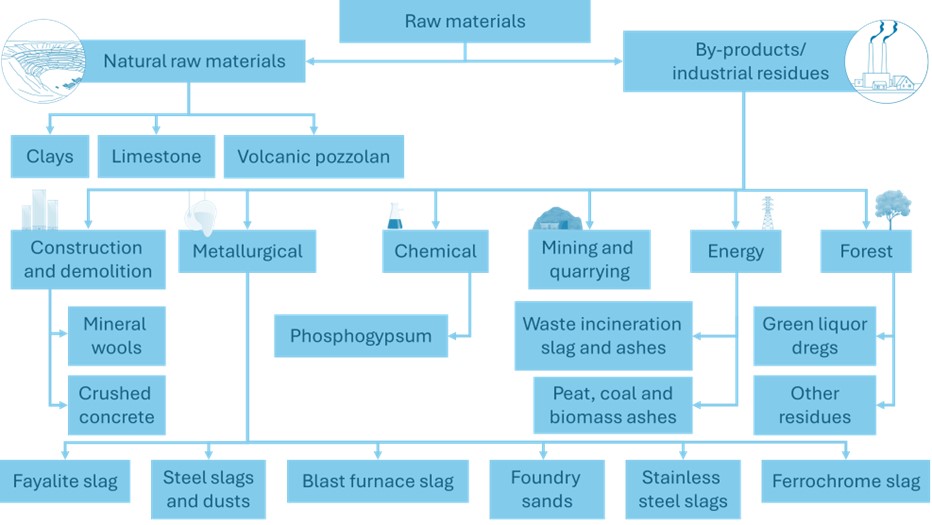
The first aspect of the project focuses on the identification of the available conventional raw materials that are currently being used in most Nordic countries for low carbon concrete. Secondary raw materials such as blast furnace slag (by-product of steel production), and fly ash (by-product of coal combustion) are the most widely used supplementary cementitious materials that are used to either partially replace clinker in cement or to replace cement in concrete mixtures.
Meanwhile the amount of these materials that will be produced in the future will reduce due to the green transition taking place in steel and energy sectors. Therefore, identifying local unconventional raw materials that could be potentially used to replace the conventional ones is of the utmost interest. In this review, different alternative non-conventional raw materials that could be used in low carbon concrete were identified. The properties of the materials and their application as construction materials were reported.
The link to the review paper can be found here: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2025.112384
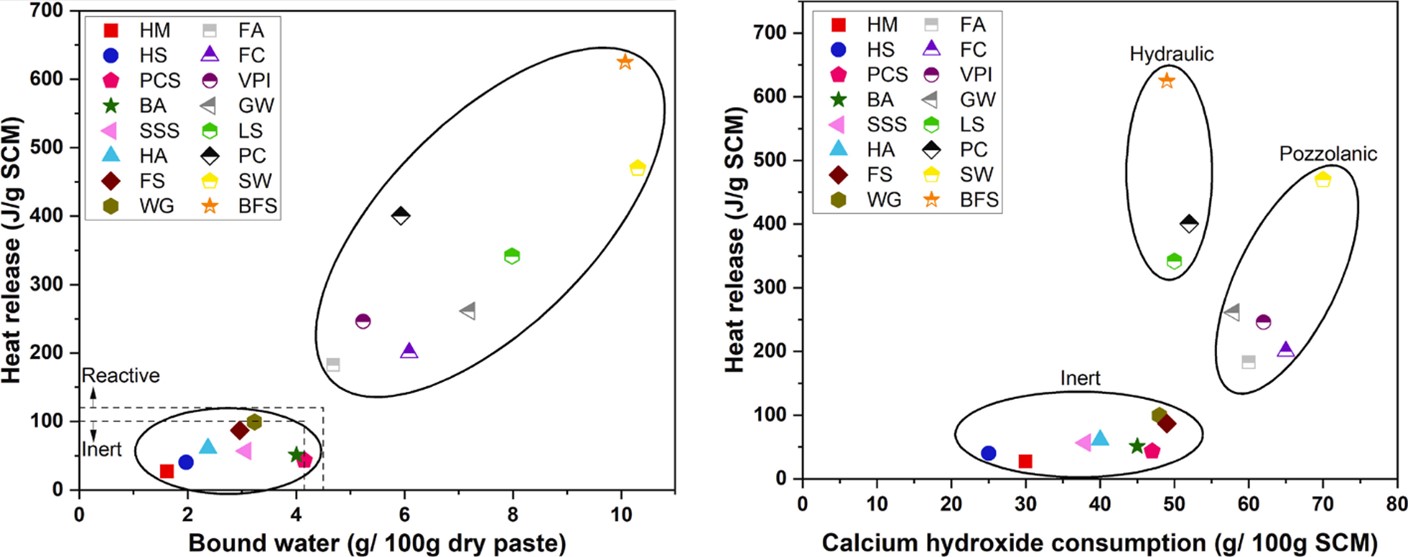
The second aspect of the project focuses on investigating the suitability of the identified raw materials as supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs) in composite cement. The composite cement was developed by replacing 30% of cement with the SCMs and they are characterized in terms of their fresh and hardened state properties. The SCMs considered are blast furnace slag (BFS), fly ash (FA), fayalite slag (FS), glass wool (GW), stone wool (SW), ladle slag (LS), municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash (BA), waste glass (WG), high silicate mine tailings (HS), high magnesium mine tailings (HM), high alumina mine tailings (HA), volcanic pozzolan Iceland (VPI), calcined Finnish clay (FC), stainless steel slags (SSS), and precast concrete sludge (PCS). The reactivity of these materials was done using Rapid, Reproducible, and Reliable (R3) test and they are classified into inert and reactive (pozzolanic and hydraulic).
The details of the study can be found here: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2025.121146